
Wednesday, January 28, 2009
Hand Drawing to Digital Painting Project
New Assignment
This time I am borrowing an assignment from another person's tutorial site. It works well.
Start with contour drawing of the item you are interested in making into a digital painting. EX- see the shoes in the hall from drawing class or anything of the cars Bo draws.
Next, scan the drawing and open it in Photoshop.
Then follow the steps in the lesson above.
Post the final work when finished.
Tuesday, January 27, 2009
Filter Assignments
ASN 2- Post the Poster you designed on Tuesday/Wednesday using Filters, Text and Blending Options.
Make sure you label each one accordingly. Great job so far.
Monday, January 26, 2009
Saturday, January 24, 2009
Filters Basics
Filters are a feature of Photoshop that gives it such power. No longer are you limited to what you can draw, paint, or import from a digital camera. You now can do RADICAL things to your images and create works of art that seem like MAGIC.
Filters can do a wide variety of things. Some simply add a slight film grain, or remove dust from a photo. Others filters can give a photo the look of an oil painting or a colored pencil drawing. Still more powerful filters can run your images through a meat grinder, wrap it in plastic wrap, or press it into wet sand.
Artistic- Painterly or artistic effects; Cutout, Fresco, Plastic Wrap
Blur- softens a selection, for retouching
Brush Strokes- Creates a variety of painting effects; Angled Strokes, Splatter, Sui-e
Distort- Geometrically distorts an image; Glass, Ocean Ripple, Pinch
Sketch- add or remove noise, dust or scratches; Despeckle, Dust and Scratches, Reduce Noise
Pixelate- breaks the image down into little dots or cells; Facet, Mosaic, Pointillize
Render- creates clouds, light effects; Clouds, Difference Clouds, Lens Flare
Sharpen- focuses blurred images; Sharpen, Sharpen More
Sketch- Adds texture to an image as if drawn in a different medium; Charcoal, Conte, Chrome
Stylize- Produces radical effects that extremely effect the image; Emboss, Extrude, Find Edges, Glowing Edges.
Texture- Gives the appearance of depth or substance, Craquelure, Patchwork, Texturizer
Filters are powerful but are also tricky. You have to learn what they all do, how much is enough and when you have gone too far. Today we will start to explore filters and their limitless possibilities. Look at the magazine cover below. It was made in Photoshop. You too will create a stylish magazine cover using a photo altered by filters.
Apply a filter
1- Choose the area you want to apply the filter to:- To apply a filter to a portion of a layer, use either the Wand or Lasso tool to select the desired area.
To apply a filter to an entire layer, deselect any selected areas (Command+D), and then select the layer in the Layers palette.
-
To use the Filter gallery, choose Filter>Filter Gallery, select a category, and click the filter you want to apply.
-
To use the Filter menu, choose Filter, then choose a submenu followed by the filter you want to apply. If a filter name is followed by ellipses (…), a Filter Options dialog box appears.
4- If available, select the Preview option to see what the filter will look like before you apply it.
5- Depending on the filter and how you are applying it, use one of the following methods to preview the filter:
-
Use the + button or - button under the preview window to zoom in or zoom out.
-
Click the zoom bar (where the zoom percentage appears) to choose a zoom percentage.
-
Click-drag within the preview window to center a specific area of the image in the window.
6- When you are satisfied with the results, click OK.
7- Remember to save your work as a JPG when complete.
8- Submit finished work to the blog. Name the entry name_filterbasics
Thursday, January 22, 2009
Tuesday, January 20, 2009
Monday, January 19, 2009
Friday, January 16, 2009
Thursday, January 15, 2009
Selection Tools
Lasso Tool
It helps to use a photo with a distinct edge. Use a digital camera and take a photo of someone in front of the white bricks out in the hallway. This makes for a perfect candidate for the Magnetic Lasso Tool because the background will be uniform.
We will start with the Magnetic Lasso for the initial selection and learn how to clean up the selection with a Quick Mask. Later we can reposition the person on a new background. With these skills we can place people in humorous locations, the moon, an erupting volcano or at the Superbowl.
In later lessons we will learn other techniques for remove backgrounds including the Background Eraser and the Pen Tool.
1- Take a moment to play with the Magnetic Lasso tool. Notice how you can create your own anchor by clicking the mouse.
2- Try opening your photo_in_text.jpg file and selecting your text by tracing it with the Lasso.
3- When you feel comfortable, move on to the Removing a Background lesson.
Now we are ready to rock and roll. You should already have your photo taken and uploaded to your computer.
1- Open the photo in Photoshop CS3.
2- Using the Magnetic Lasso drag along the edge of an object. The tool will create a selection line along the path as you go. At key edges you may drop your own anchor by clicking the mouse.
!!! If you get an anchor that is out of position, do not freak! Just click on the DELETE key and it will step back a step.
3- Once you have come completely around the figure, click once to close the selection. You know have your person selected. You will undoubtedly find little places where the Lasso missed a spot or two. We will fix that in the steps 4-8.
As you can see, the Magnetic Lasso was not perfect. It sometimes fails to detect the object around complicated spots like the hair. We can correct this fairly easily by zooming in and switching to Quick Mask mode.


In quick mask mode, your image is displayed with a red overlay. It represents the masked area. In this mode, your tool palette only displays white and black for the foreground and background colors. Painting with white takes away from the ruby overlay to subtract from the mask, and painting with black adds to the ruby overlay to add to the mask.
4- Click on the Quick Mask button on the toolbar to switch into quick mask mode.
5- Zoom in to where your image needs correcting.
6- Painted away the ruby overlay to reveal the parts of the subject that need to be included in the selection.
!!! Tap the space bar to temporarily bring up the Hand tool to nudge the image over if you come to the edge of the screen.
7- While still in Quick Mask mode apply a half-pixel Gaussian Blur to the mask just to soften the edge the slightest bit. Any filters you apply in quick mask mode will only effect the mask and not the image itself. Filter> Blur> Gaussian Blur
8- After applying the blur effect switch back into selection mode by pressing Q or using the toolbar toggle button.
9- In the photo layer choose Selection>Invert and the
10- Press delete on the keyboard to remove the old background.
11- Save the image as background_cutout.psd before moving on.
Now its time to insert the subject in a new background. This shouldn't be a problem if you remember how to drag a photo onto an image like you did in the Photo In Text lesson.
1- Open the photo you wish to use as your new background.
2- In the photo layer of your background_cutout.psd project, use the Move tool to drag the figure onto your background.
3- Resize your figure using Command>T. You can hold down SHIFT to constrain proportions while resizing.
4- When finished, save as jpg.
Wednesday, January 14, 2009
Tip: Managing Layers
Also, to unlock the BACKGROUND layer and make it editable, simply double click on it and Photoshop renames it Layer 0. Now you can drag it around, edit it, even delete it if you wish.
Tuesday, January 13, 2009
Friday, January 9, 2009
Photo Behind Text Project

In this assignment you will create a banner with a neat photo-in-text effect.
1- Open Photoshop CS3. File>New. Name the project "photo_in_text"
2- Using the Type tool, type the text you wish to use.
3- Change the font to match your design. A bold typeface works best. Hold down Command key to change the font size with the mouse.
4- Open the Photo you wish to place in the text.
5- With the Move tool drag the photo to the file with the text.
6- Position the photo on the text the way you want with the Move tool.
7- In the photo layer, choose Select>All
8- Choose Edit>Cut
9- In the text layer, choose Rasterize Text from the Layers Options.
10- Using the Wand tool, capture the first leter from your text.
11- Choose Select>Similar so all of the text is selected.
12- Choose Edit>Paste Into
13- You can use the Move tool to reposition the photo within the letters. Make sure you are in the combined layer.
14- Try adding addition effects like Drop Shadow on the Bledning Options.
Save final image as a jpg.
Keep a Tidy Workspace
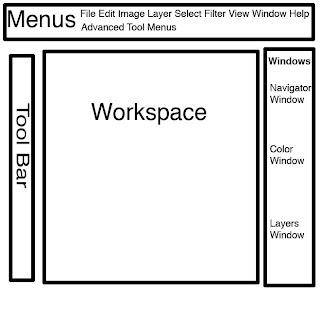
Keeping an organized workspace is essential for a beginning Photoshop artist. Here are some basic tips to keep you from getting lost in all the options.
There are FOUR MAIN areas to work from. Keep them in the same location.
- Menus- Drop-down menus like File, Edit, Select, etc.
- Tool Bar- Think of this area as your box of drawing supplies, pens, paintbrushes, erases, etc.
- Workspace- This is your canvas; where you draw, paint, edit.
- Windows- Color pallet, layers window and navigator are kept here.
Thursday, January 8, 2009
What is Photoshop?
A popular high-end image editor for the Macintosh and Windows from Adobe. The original Mac versions were the first to bring affordable image editing down to the personal computer level in the late 1980s. Since then, Photoshop has become the standard in image editing. Although it contains a large variety of image editing features, one of Photoshop's most powerful capabilities is layers, which allows images to be rearranged under and over each other for placement.
Wednesday, January 7, 2009
Brush Modes
1- Multiply: Treats the image like a coloring book page. It will cover up white but not the existing colors. It is great for taking black and white images and coloring them, either realistically, or in amazing neon colors.
2- Color Burn: burns colors onto the image. Colors get darker the longer you hover over an area.
Brush Mode Project
1- Open image in Photoshop
2- Image> Adjust> Desaturate
This makes your image black and white.
3- Select the Brush tool. Change the Mode to Mulitply (or Color Burn). Select the desired color from the color pallet on the bottom of the tool bar.
4- Experiment painting the image.
5- Saved finished project as a JPED (.jpg) and follow Mr. Bollman's instructions on how to submit the finished work to the Blog.
Format Questions
1. Which format should you save your image in if you are not finished with it and you may need to edit font or a layer in the future?
2. Which format should you save your image in if you are finished with it and are ready to share it on the web?
3. Which format should you save a completed flyer or poster in if you want to share it on the web?
4. Which format allows transparent backgrounds?
5. When you save files off the internet, what is a good way to keep track of them so you can work with them in the future?
Tuesday, January 6, 2009
JPG- Joint Photographic Experts Group
A universal file format the compresses an image very small and makes it easy to share on the Internet and on a variety of computer platforms.
PSD- Photoshop Document
A file format created by Adobe that is very large and includes layers and paths. It is editable but not shared easily on the web or from computer to computer. IT IS NOT UNIVERSAL!
PDF- Portable Document Format
A universal document format allowing easy sharing and printing of documents on the web and from computer to computer. In ofter flattens images so they are no longer editable.
TIFF- Tagged Image Format
A universal photographic format that allows for transparent backgrounds. It is not editable.
Monday, January 5, 2009
Assignment 1
Graphic Design
Digital Imaging
Adobe Photoshop
Commercial Art
Branding

































